Elevating Sustainable and Cost-Effective Design Initiatives With Additive Manufacturing
Key Takeaways:
- Additive manufacturing cuts material waste, potentially lowers carbon emissions, and accelerates production
- aPriori simulates additive manufacturing, enabling companies to optimize design, cost, and sustainability
The Full Article:
Design engineers worldwide increasingly turn to additive manufacturing (3D printing) to reduce waste, cut raw material usage, lower costs, and minimize production delays. While initially embracing 3D printing technology for rapid prototyping capabilities that enable necessary design iterations, they are now exploring additive manufacturing to achieve cost, sustainability, and time-to-market goals.
As more designers recognize 3D printing’s benefits, projections show that the additive manufacturing market will grow at a 20.8% CAGR from 2023 to 2028.
Discover how 3D printing enables designers to achieve product design excellence and explore the differences between additive manufacturing and traditional manufacturing:
- Additive Manufacturing vs. Traditional Manufacturing
- Four Key Advantages of Additive Manufacturing for Product Design
- How Additive Manufacturing Solves Manufacturers’ Challenges
- More Incentives to Adopt Additive Manufacturing
- Leverage the Power of aPriori’s Additive Manufacturing Process Models
- Unlocking the Potential of Additive Manufacturing
Additive Manufacturing vs. Traditional Manufacturing
Traditional manufacturing methods produce cheaper but heavier parts at high volumes. However, for low-volume production, machining, casting, or similar processes significantly increase per-unit costs. Depending on the product or part, a different design and manufacturing approach is necessary. This often involves starting with a large price of material and shaping it to the required part or desired form.
The traditional approach focuses on subtractive manufacturing, whereas additive manufacturing creates parts or shapes by adding material layer by layer through 3D printers. This method utilizes 3D computer-aided design (CAD) software to turn product ideas from designs into physical items. They employ CAD technology to create 3D models (virtual representations of products) and ensure their printability.
Product development teams can harness the functionalities of additive manufacturing to boost innovation, reduce waste, and minimize the need for post-processing. They can also adopt a hybrid strategy that combines both additive and traditional methods or transition completely to an additive-based approach.
Listen to our podcast to learn if additive production and 3D printing processes suit you.
Four Key Advantages of Additive Manufacturing for Product Design
There are four opportunities for design engineers to find value in additive over traditional manufacturing when meeting manufacturability, sustainability, and cost initiatives:
- More design flexibility: Additive manufacturing enables manufacturers to create nearly any 3D shape or complex geometries, providing design engineers with more design freedom and flexibility. Boeing’s aerospace division efficiently produced a bracket for its 787 Dreamliner using additive manufacturing, reducing the “buy-to-fly” ratio by 85%.
- Greater customization: Reducing reliance on molds and fixed tooling allows for more component customization. This flexibility provides opportunities to utilize higher-performance, lightweight materials, which might be too expensive with traditional methods. A reduction in waste and improved performance can lead to more cost-effective manufacturing. This advantage becomes particularly crucial during supply chain and material shortage issues.
- Faster time to market (TTM): Unlike traditional manufacturing approaches, additive production eliminates the need for time-consuming fabrication or toolmaking. Consequently, it makes new product development (NPD) more efficient and faster, enabling teams to eliminate late-stage, costly redesigns and accelerate TTM.
- On-demand parts, less inventory: Additive production requires fewer parts to create a product, consequently reducing the need for large inventories of spare components. This is especially crucial in the automotive industry, where manufacturers produce a vast amount of parts in mass quantities and store inventory across multiple locations.
How Additive Manufacturing Solves Manufacturers’ Challenges
Manufacturers aiming to stay competitive amidst design and production hurdles are embracing additive production to tackle current and future obstacles in the following areas:
Manufacturability
Additive manufacturing technologies allow manufacturers to reduce the number of parts produced and their inventories. Design and production time could potentially be reduced due to fewer required materials and processes to create those parts. However, they can have more iteration flexibility since it doesn’t require the lead time that tooling necessitates.
Sustainability
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) reports that manufacturers switching to additive manufacturing can reduce waste by up to 90% and lower energy use by 25%. The key sustainability benefits of the additive manufacturing process include its ability to:
- Require fewer materials, significantly reducing waste
- Eliminate the need to produce tooling
- Reduce carbon by lowering reliance on far-flung suppliers and supply chains
- Enhance fuel efficiency through the production of lighter-weight parts
- Boost local manufacturing and sustainability efforts through on-demand manufacturing
- Facilitate manufacturing processes closer to where they are needed, reducing transportation requirements
Profitability
Manufacturers aim to maximize productivity and profitability with fewer resources. Since the design phase determines 80% of a product’s cost, additive manufacturing’s flexibility enables the quick, localized, and cost-effective redesign of complex parts. This method also allows manufacturers to produce low-volume components at a lower cost.
The U.S. DOE has revealed that additive production helps companies cut expenses like material costs by 90%, further boosting their profitability.
More Incentives to Adopt Additive Manufacturing
The Federal Government is implementing financial incentives through the Inflation Reduction Act to support the optimization of manufacturer sustainability efforts. The Act includes $370 billion in spending and tax incentives on energy and climate change provisions. These provisions are intended to spur investments not only from traditional energy companies but also from transportation, real estate, and manufacturing sectors.
The Section 48C Manufacturing Tax Credit proposes expanding this credit to include advanced energy properties that reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, as potentially determined by the IRS. It might also apply to properties upgrading existing infrastructure to reduce GHGs by at least 20%, potentially opening the path for advanced technologies to take advantage of these credits.
Leverage the Power of aPriori’s Additive Manufacturing Process Models
aPriori’s automation-driven platform provides more than 440 Manufacturing Process Models (MPMs), including additive manufacturing, enabling teams to simulate production. aPriori’s simulation engine breaks down 3D CAD design into geometric cost drivers (GCDs) for precise, quick analysis of part cost, carbon dioxide equivalent emissions (CO2e), and manufacturability. Moreover, product development teams can determine the most optimal manufacturing routing.
Product teams can use aPriori’s robust MPMs to evaluate multiple additive manufacturing methods down to the machine level, including:
- Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
- Material Jetting (3D printing)
- Powder Metal
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- Stereolithography (SLA)
What Outcomes Can Product Teams Anticipate Using aPriori Manufacturing Insights?
By using aPriori’s Manufacturing Insights Platform, equipped with robust MPMs, product teams can successfully:
- Eliminate late-stage engineering change orders (ECOs) and accelerate time to market
- Evaluate how design and material changes impact cost, CO2e, manufacturing cycle time, and sourcing decisions
- Identify and eliminate product cost drivers early in the production process to hit cost targets
- Use detailed should cost estimates and reports to negotiate with suppliers and capture savings
- Improve cross-functional collaboration by centralizing manufacturing data that can be acted upon
- Utilize dashboards and reports to keep leaders updated on project statuses, material usages, and cost outlier analysis
- Assess multiple supplier options to select suppliers based on regional labor rates, energy usage, raw material costs, and more
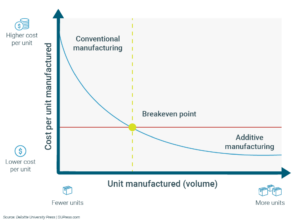
Lastly, aPriori enables manufacturers to identify the breakeven point. The platform immediately costs a traditionally manufactured part and compares it to one produced by additive manufacturing at specific volumes. These insights will then determine the volume point at which traditional high-volume methods are best. It will also relay the below volume point where additive manufacturing can be used instead.
Unlocking the Potential of Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing is transforming product design and production through its flexibility, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. aPriori’s automated platform enhances this transformation, providing cost, manufacturability, and sustainability analyses to help product development teams optimize their processes.
A Guide to Reducing Product Carbon Emissions
Learn how to identify hidden CO2e emissions during product design to achieve net-zero goals!