A McKinsey article revealed that up to four-fifths of a product’s lifetime emissions are determined at the design stage. Further analysis found that although 5% or less of a product’s total cost is attributed to research & development (R&D), it has a profound impact on the product resource footprint of up to 80%. Sustainable product design along with manufacturing insights offers an efficient method to measure, reduce, and report on a product’s carbon dioxide (CO2) footprint.
This article will outline a product design’s impact on costs and the carbon footprint. We will emphasize the importance of considering factors beyond the actual product’s function to ensure a more sustainable product design including its end-of-life.
What is Sustainable Product Design?
There are many definitions of “sustainable manufacturing.” For example, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) defines it as ”the strategic method of creating products through economical means and using components that minimize waste and reduce negative environmental impact.” For the purposes of this article, we believe sustainable product design can be made much more accessible and impactful by utilizing automated geometry-driven analysis of 3D CAD data to create products and evaluate their carbon footprints.
Sustainable product design and manufacturing can play important roles in fostering more sustainable development. According to the World Commission on Environment and Development, the ultimate goal is to “meet the needs of the present, without compromising the capability of future generations to meet theirs.”
The good news is that more companies acknowledge that sustainability is not only important but can be beneficial to their growth and competitiveness in the marketplace. According to KPMG’s 2020 Survey of Sustainability Reporting, 80% of the world’s leading companies are now incorporating sustainability initiatives into their operations and goals.
This uptick is crucial to the world’s ecosystem. Recently, the World Meteorological Organization issued a press release, declaring that atmospheric levels of the three main greenhouse gases (GHGs) – carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide all reached new record highs in 2021. It portends an even more urgent call to decarbonize our operations, calling for a more rigorous push to ensure that manufacturers have the solutions to reduce GHGs to further stem accelerating climate change. A manufacturing insights solution that calculates CO₂ equivalent emissions is critical to this goal. CO₂ equivalent (CO₂e) is the number of metric tons of CO₂ emissions with the same global warming potential as one metric ton of another greenhouse gas.
Become More Transparent, But Leave a Smaller Footprint
What capabilities and features should a product sustainability solution offer? In short, several that will enable manufacturers to achieve sustainability goals. Here are six metrics that can facilitate sustainability:
- Sustainable Modeling: It is based on the principle of creating a sustainable value proposition for customers and stakeholders. It does not compromise, or further negatively impact, the environment, economy, or society. Ideally, it will create economic value for the organization and maintain or regenerate resources beyond it. It is accomplished through:
- Baselining: To make improvements, manufacturers need to establish a baseline centered on a previous generation of, or their current, products. From a sustainability perspective, this essential factor entails understanding the product’s environmental impact. If sustainable product design is the objective, then it should be prioritizing GHGs/CO₂e reductions.
A good first step is to identify CO₂ outliers and how they impact reporting. By focusing on one product aspect, improvements are made more easily and efficiently. Without baselining your product lifecycle in an accurate and meaningful way, then you run the risk of being accused of “greenwashing” (making people believe your organization is doing more for the environment than you are in reality).
- Optimization: Once you understand your product’s environmental impact, there’s more to it than addressing where you can be more sustainable. Successfully sustainable manufacturers will take it a step further, not only mitigating issues but also optimizing their products as part of continuous improvement. Manufacturing insights allow you to optimize components for cost and CO₂ equivalents while ensuring manufacturability. Through sustainable product design, manufacturers can improve the value, reduce costs and improve manufacturing profitability, and turn out a more environmentally friendly product with a lower carbon footprint.
- Design for sustainability: Itis focused on reducing resources and waste throughout a product’s creation and lifespan including raw materials and manufacturing processes that impact the environment. Design for sustainability considers a product’s end of life as well. Can it be recycled, reused, or repurposed? It should be manufactured so it is reusable, serviceable, and recyclable. Easy-to-recycle materials should take precedence. For instance, all metals can be recycled but not all plastics. Even better, use recycled materials early in the product development stage. Use fasteners instead of adhesives, which can be taken apart more easily. Ideally, there should be an opportunity for each component to be remanufactured, recycled, or reused.
Typically, designers don’t consider a product’s end of life. Some product designs encourage repeat sales or planned obsolescence. Our smartphones are a good example. They are discarded in lieu of a newer, better upgrade. Designers can leverage manufacturing insights to ensure more sustainable product design that reduces waste, lowers its carbon footprint, and reduces its GHGs. These metrics can facilitate the process:
- Trade-off analysis: How can manufacturers design products that lower the carbon footprint without compromising the product? Trade-off analysis can compare which materials, processes, and shapes can be used for more sustainability. This CO₂ footprint analysis can be conducted through digital factories, with full visibility into cost and manufacturability. More informed decisions can be made to reduce environmental impact based on the analysis. Customers’ product needs and desire for more sustainable products are met by providing a CO ₂e footprint breakdown to analyze and implement sustainability actions.
- Manufacturing insights: These insights allow designers to reduce environmental impact through more sustainable design engineering. Early design process feedback on flaws, excess waste, higher energy requirements, and more can help reduce a manufacturer’s carbon footprint. aPriori provides fast, automated geometry-driven analysis for 3D CAD data to evaluate the carbon footprint, reducing late-stage redesigns and identifying opportunities to lower CO₂ emissions early in the product development cycle. These insights and analytics can be used to track and quantify sustainability initiatives with stakeholders and investors as well.
- Sustainable Manufacturing & Scope 3: Sustainable manufacturing is the creation of manufactured products cost-effectively and via processes that reduce environmental impacts, while conserving energy and natural resources.
To use the same definition as the EPA, Scope 3 emissions, also known as value chain emissions, are the result of activities from assets not owned or controlled by the reporting organization but that the organization indirectly impacts in its value chain. They often represent the majority of an organization’s total GHG emissions including both upstream and downstream of the organization’s activities. Leveraging the following insights supports sustainable product design:
- Supplier Data: Compare suppliers’ environmental impact based on their geographic location. With information from our Regional Data Libraries, manufacturers can utilize local and geographically closer suppliers. As a result, they can significantly lower their carbon footprint and mitigate supply chain issues. Moreover, better supplier relationships mean more opportunities to identify and work with those who provide sustainable materials, parts, and processes, further bolstering the manufacturer’s sustainability credentials.
- Material Waste Reduction: Reduce material waste based on process and evaluate materials’ GHGs. All will go a long way to supporting more sustainable products and resource efficiency. Technologies such as aPriori facilitate more efficient and cost-effective sustainable product design. aPriori has helped customers create as much as 3-5 times more projected CO2savings with their design for sustainability insights.
Implement Sustainable Product Design as a Best Practice
Sustainable manufacturing is gaining momentum. Manufacturers are recognizing the importance of measuring efficiencies and meeting goals. To fully harness and maximize its power, design engineers can implement the following sustainable product design best practices:
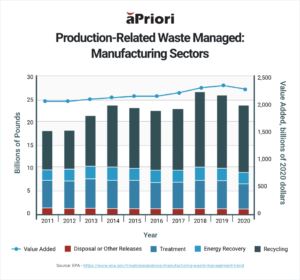
- Reduce waste from design through production: According to an EPA Manufacturing Waste Management Trend report, in 2020, only 5% of the manufacturing sectors’ production-related waste generated was released into the environment. The rest was managed through treatment, energy recovery, and recycling. Sustainable product design can play an integral role in reducing waste through these methods. Processes primed for waste reduction can be identified, or potentially cut out altogether, early in the design stage. See the above graph.
- Revisit energy consumption and sources: The American Meteorological Society noted in their 32nd State of the Climate report that GHGs concentrations, global sea levels, and ocean heat content reached record highs in 2021. Manufacturing insights can pinpoint unnecessary, energy-sapping materials and processes as well as provide more environmentally friendly alternatives.
- Reevaluate facility usage: 54% of the world’s energy consumption is from manufacturing. Modifications in operations via manufacturing insights also can reduce excess waste and help identify more efficient production processes. Improving production efficiencies means less time in the factory, translating into less energy usage and less cost.
- Recycle, repurpose, or reuse materials: 80% of a product’s early design determines its environmental impact. Recycling is the most basic but also the most important green manufacturing process. An effective recycling system can help companies reduce waste and have a positive environmental impact. Using secondary or recycled materials is a better option vs. recycling current materials.
Use manufacturing insights at the design phase and rely on more sustainable materials. You will create more environmentally friendly products that help lower your carbon footprint.
By utilizing manufacturing insights and incorporating sustainability best practices, you’ll create a truly sustainable business that will have a profound impact on the environment now and for future generations.
Discover what design for sustainability can do for you
80% of a product’s early design determines its environmental impact. Learn more on how to reduce that impact.