How Designers Can Quantify Additive Manufacturing Benefits
With an eye on greater profitability and sustainability, manufacturers are exploring alternative modes of manufacturing. Some are recognizing additive manufacturing benefits. This article revealed the past two years have been the most active investment period on record for such companies.
As a design engineer, you can play an integral role in quantifying the value of capital investments in additive manufacturing. You can utilize your technical expertise and innovative spirit to facilitate a seamless transition to this technology. Best of all, you can be a significant factor in improving profitability for your enterprise.
In this article, we will explain the additive manufacturing benefits and the capital investment trends in this area. We will cover five ways you can help quantify the feasibility of capital investment in it to your management team
More 3D Printer companies are experiencing increased venture capital investments. Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D Printing, usage is growing exponentially faster than traditional manufacturing methods. According to a 3D Printing Industry article, it will be considered THE manufacturing technology that will support a sustainable and resource-efficient society within the next 10 years.
For those enterprises seeking related capital investments, employing a simple cost per part estimate does not illustrate the full investment picture. This is where you come in. You can provide valuable insights that underscore the value of additive manufacturing and quantify the ask with upper management.
What is Additive Manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing takes a computer-aided design (CAD) and translates it into a layer-by-layer framework. It will use this framework to create and then send to a 3D printer. It then builds up each layer, creating the physical object on the spot. There are seven main types of additive manufacturing or 3D printing including: VAT Photopolymerisation, material jetting, binder jetting, powder bed fusion, direct energy deposition, sheet lamination and material extrusion. The terms “additive manufacturing” and “3D printing” are used interchangeably.
The beauty of additive manufacturing is that it requires no physical machine tooling. Substances such as plastics, resins, metal, carbon, and powder can be printed with additive manufacturing. Manufacturers in various industries – including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer and industrial goods – employ it.
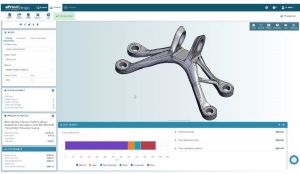
aP Design machined part redesigned for additive with a cost breakdown
Additive Manufacturing Benefits
Understanding the additive manufacturing benefits is essential when quantifying capital investments. Below are five ways you can quantify the benefits of a capital investment in additive manufacturing with stakeholders:
- Cost Reductions: Cost is always at the forefront of the vast majority of manufactured parts. When considering the true cost of a part, it is important to factor in all aspects (labor, materials, tooling, etc.) Cost alone though does not make a case for additive. If they concentrate on labor, materials, or post-processing, and you could potentially argue that using 3D printing would help drive those costs down. A good manufacturing simulation platform can help you examine the most cost-effective designs for additive. Each part’s volume and material quantity can be reduced, lowering material costs as well. Arguably, it can generate any 3D component. However, it is always better to optimize the design for the process. Simply printing a design meant for another process will rarely yield the full benefits. In many cases, it has the potential to perform better and cost less than conventional manufacturing methods. It also reduces the need for spare parts inventories, enabling parts production from digital files, on demand and in the field.
- Performance factors: Your technical expertise makes you uniquely qualified to justify additive manufacturing benefits over traditional manufacturing. Design for additive rules are not well known, varying considerably between its seven different families. They also can vary from vendor to vendor. A solid design for manufacturability (DFM) platform can provide valuable additive guidance after consolidating parts or light weighting them. For example, when designing an aerospace or auto part in a DFM platform, you will have visibility into how additive results in a lighter, higher performance part, with a far superior buy-to-fly ratio. These results offer a strong story supporting the use case for additive.
- Supply chain disruption mitigation: For the past few years, supply chain problems have been a thorn in the sides of manufacturers. Additive manufacturing can be the salve. These disruptions clear a path for it to develop more customized products and/or get them to market faster. You can facilitate this process, and can help reduce the number of parts necessary to make a product. As a result, there is less reliance on multiple suppliers for parts and materials as well as lower assembly costs.
- New Growth Opportunities: New market and growth opportunities abound. Additive manufacturing can be a key factor in reshoring manufacturing operations, determining its cost-effectiveness. Along with your experience, it can help plan and develop future parts and assemblies. New opportunities for expansion can be created that might not have been possible without it or your knowledge. You can offer value proposition feedback, paving the way for more innovation and future growth. Since fixed tooling and molds are unnecessary in additive manufacturing, the sky is the limit in customizing parts and assemblies on a larger scale.
- Printable Parts Identification: Additive manufacturing is charting new territories. However, it does not make sense in all cases. Leverage your skillset to determine which parts are too expensive or impossible to machine. Then recommend those best printed instead. Additionally, take a comprehensive approach. Rather than focusing solely on parts, consider the entire assembly or system. As a result, you can add functionalities and combine various parts in a more innovative, cost-effective manner that traditional manufacturing cannot support.
One Additive Manufacturing Story
Famously, GE was able to reduce the weight of a fuel nozzle by 25 percent with additive manufacturing. Naturally, weight reduction is crucial in aerospace applications. It is advantageous not only from a safety standpoint but also because it enables them to carry heavier payloads, go farther on less fuel, and account for additional functionalities. It also reduces costs significantly.
The company was able to eliminate the tooling of an engine’s structural castings. Opting to use additive manufacturing to create the engine reduced development time by almost 50%. By removing the more time-consuming functions of traditional manufacturing, enterprises can get to market faster and more cost-effectively. Additionally, they were able to reduce 900 parts to 20 parts as a result of moving to it.
The above scenario is illustrative of its power and why manufacturers should invest in it.
Conclusion
Disruptive technology can be difficult to quantify from a capital investment standpoint. It is harder to conceptualize the full scope and potential of such newer technologies. Although it requires you as the design engineer to stretch your mind regarding the possibilities of additive manufacturing, it also can reignite your passion to explore more capital investments in the area.
It is here to stay. The time is now to invest in its competitive, design, and financial advantages. You can be an invaluable ally in this step forward. Who understands new and exciting innovations better than a design engineer? The technical expertise and passion you bring can mean the difference between securing those capital investments and remaining a viable entity or staying mired in traditional manufacturing methods.
What are you waiting for?
The time is now to turn to additive manufacturing